Rhabdoid Tumor : Role of SMARCB1 (INI1)

Comments:
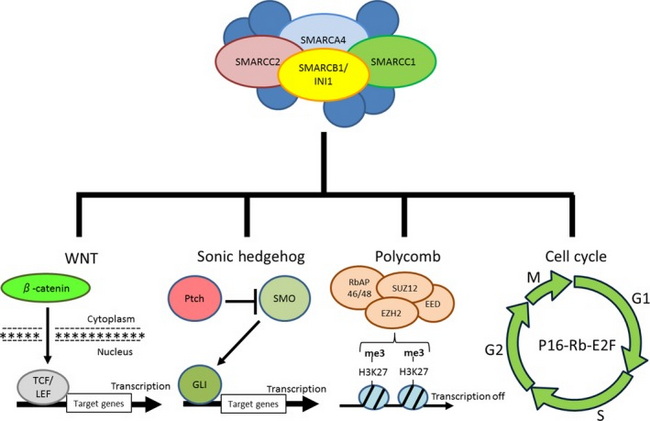
Molecular Genetics: Renal and extrarenal rhabdoid tumors are characterized by homozygous inactivation of SMARCB1 - a tumor suppressor gene (also known as INI1, BAF47 or hSNF5) on chromosome 22q11.23. Cytogenetic studies have shown karyotypic abnormalities of 22q11-12 region in most rhabdoid tumors. SMARCB1 is ubiquitously expressed in the nuclei of all normal cells. The recommended nomenclature is SMARCB1 (SWI/SNF related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily B, member 1) and replaces human sucrose nonfermenting gene number 5 (hSNF5), integrase interactor 1 (INI1), or 47-Kd Brg1/Brm-associated factor (BAF47). SMARCB1 protein makes up one core subunit of SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex which plays a critical role in epigenetic regulation, cell cycle progression and crosstalk between signaling cascades as discussed in the next several images. Loss of SMARCB1 causes carcinogenesis via epigenetic activation and repression of several key genes. The image shows target genes and signaling pathways implicated in the tumor suppressor action of SMARCB1. Image source: Kohashi K & Oda Y. Oncogenic roles of SMARCB1/INI1 and its deficient tumors. Cancer Sci 108 (2017): 547-552; used under Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.



