Cellular Neurothekeoma : Differential

Comments:
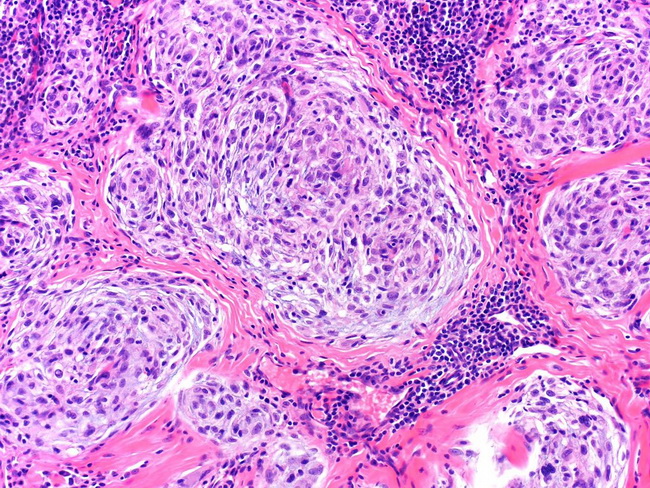
The differential diagnosis of neurothekeomas depends upon the amount of myxoid stroma and includes the following entities. Plexiform fibrohistocytic tumor (PFHT): A biphasic tumor composed of fascicles of spindle cells (resembling fibromatosis) around nodules of histiocytes and osteoclast-like giant cells. Microphthalmia transcription factor (MiTF) is expressed in neurothekeoma but not in PFHT. Reticulohistiocytoma: This is seen in older patients as compared to neurothekeomas and lacks plexiform whorling patterns. Epithelioid Fibrous Histiocytoma: It occurs more frequently in the leg and shows an epidermal collarette. Melanocytic tumors: They are positive for S-100 protein and melanocytic markers (HMB45, Melan-A). Neurothekeomas are negative for these markers. Myxoid soft tissue tumors: Extensively myxoid neurothekeomas may mimic nerve sheath myxoma, superficial angiomyxoma, or myxofibrosarcoma. Image courtesy of: Rami Al-Rohil, MBBS, Department of Pathology, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, USA; used with permission.



