Extranodal Rosai-Dorfman Disease : Bone

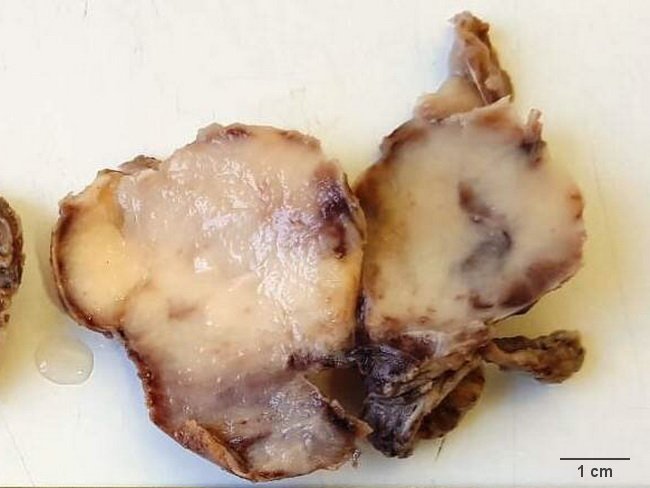
Comments:
Extranodal sites are involved in 25% to 40% of cases of Rosai-Dorfman disease. The disease has been reported in virtually every body site/tissue. The most common extranodal sites include skin, central nervous system, upper respiratory tract, orbit, bones, breast, salivary glands, and gastrointestinal tract. Case History: This is a specimen of extranodal Rosai-Dorfman disease involving bone. The patient was a 35 y/o female who presented with a chest wall mass and was found to have an expansile lytic lesion involving 5th rib. It consists of a 8 x 5 x 2.5 cm poorly-circumscribed mass with grayish-white, nodular fleshy surface. Sections showed an infiltrative mass composed of histiocytic and lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. There was prominent emperipolesis and erythrophagocytosis. Case courtesy of: Sunita Kolekar-Samleti, MD, Dept. of Pathology, Apollo Hospital, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India.



