Coccidioides : Life Cycle

Comments:
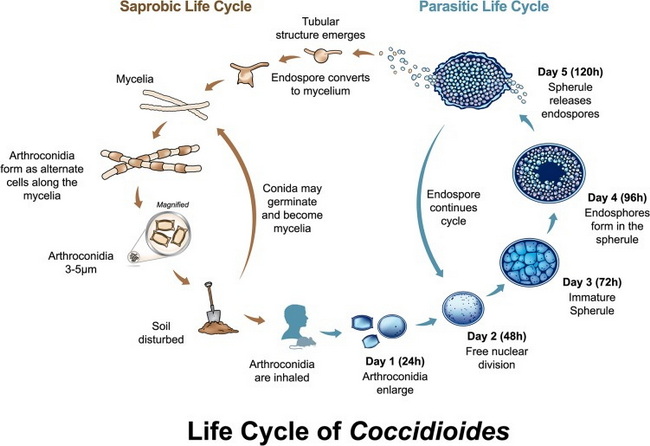
Life Cycle of Coccidioides spp.: Both Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii have a well-characterized asexual life cycle with saprobic and parasitic stages.Saprobic stage occurs in the environment and the fungus cycles between the filamentous mycelia and the infectious, barrel-shaped arthroconidia. The arthroconidia may stay in the soil and continue the saprobic life cycle OR they may be inhaled by a host and enter the parasitic stage.Parasitic Stage: When the soil is disturbed by weather, construction, earthquake, or similar events, the arthroconidia get airborne and are inhaled by a susceptible host. This initiates parasitic stage, usually in the lung. Within 24 hrs., the arthroconidia start developing into immature spherules which grow, septate, and develop endospores. This is followed by rupture of mature spherules and release of endospores (see diagram). Each endospore can develop into a new spherule, thereby propagating the infection cycle. The endospores can also develop into septate branching hyphae and barrel-shaped arthroconidia, usually in the environment and rarely within a living host. Image Source: Lewis ERG, Bowers JR, Barker BM. Dust Devil: The Life and Times of the Fungus That Causes Valley Fever. PLoS Pathog. 2015 May; 11(5): e1004762; used under Creative Commons Attribution License.



