Lepromatous Leprosy : Clinical Features

Comments:
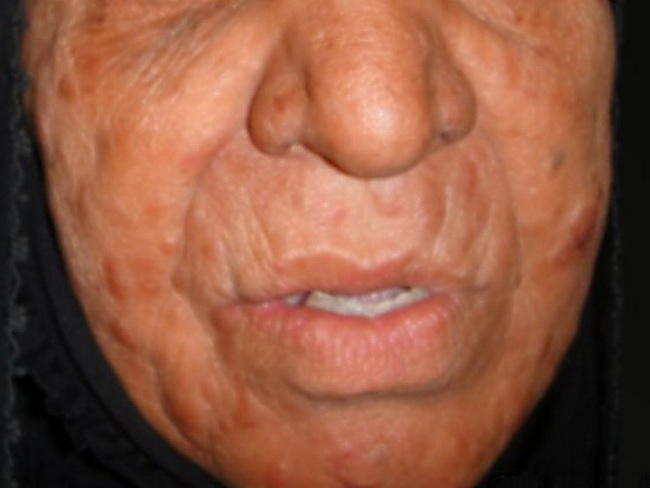
Lepromatous leprosy is a more systemic and widespread disease as compared to the tuberculoid form and is seen in patients with poor cell-mediated immunity to M. leprae. The antibody titers to M. leprae are high. The skin lesions are multiple, widespread, symmetrical, and firm and include a combination of macules, papules, plaques, and nodules. They tend to be located on acral sites which are cooler such as earlobes, face, tip of nose, and back of hands. Facial lesions cause loss of eyebrows. Destruction of nasal bone and cartilage may cause saddle nose. Axilla, perineum, and groin are typically spared. Nerve involvement causes muscle wasting and sensory loss which can result in claw hand and foot drop respectively. Case History: This photograph shows a 65 y/o female with more than 5-yr history of skin-colored firm papules and nodules involving many parts of the body in a symmetrical way. The face had the most striking features in the form of general leonine waxy appearance, loss of the eyebrows (madarosis) and eyelashes, and large number of ill-defined skin-colored nodular infiltrations. Skin biopsy revealed typical histological features of lepromatous leprosy. Image courtesy of: Nameer Al-Sudany, MD; Global Skin Atlas; Used with permission.



