Primary Effusion Lymphoma : Pathogenesis

Comments:
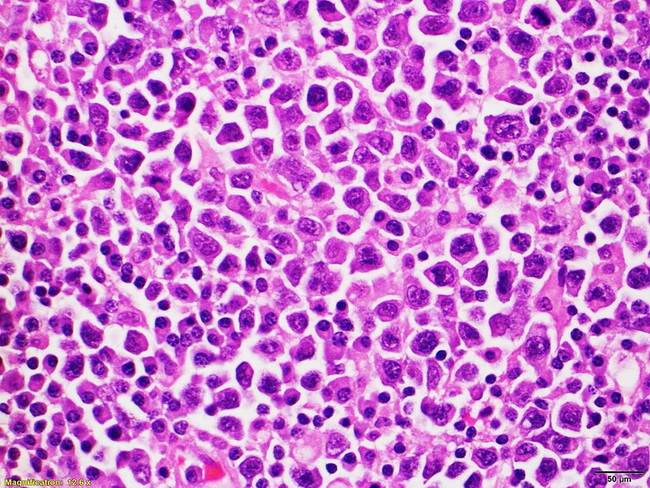
Pathogenesis: Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8), also known as Kaposi Sarcoma Herpes Virus (KSHV) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). Adult males with AIDS are particularly at risk. One third of patients with PEL also have Kaposi sarcoma. Viral particles can be demonstrated by PCR, electron microscopy (100-115 nm particles within nucleus and cytoplasm of neoplastic cells), or immunohistochemistry (antibody to LANA or viral IL6). Most cases of PEL in the setting of HIV infection are co-associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV); in other words, PEL involves 3 viruses - HHV8, HIV, and EBV. However, EBV is not required for the pathogenesis. EBV-negative PELs have been reported in elderly HIV-negative patients from HHV8 endemic areas such as the Mediterranean. HHV8 genome has been shown to contain two oncogenes. One is homologous to CCND1 oncogene (implicated in mantle cell lymphoma) and the other is similar to the cellular G protein-coupled receptor (GCR) family of proteins. The photomicrograph is from a case of HHV8-positive, EBV-negative diffuse large B-cell lymphoma resembling a PEL. Image courtesy of: Siba El Hussein, MD; used with permission.



