Black Pigment Gallstones : Pathophysiology

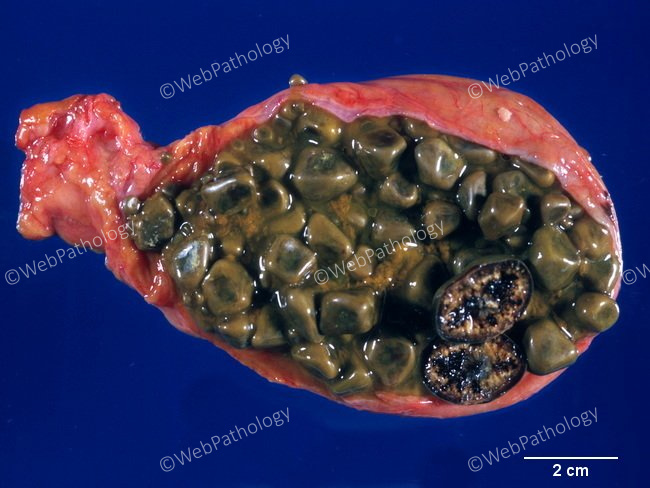
Comments:
Black Pigment Gallstones - Pathophysiology (continued from the previous image): Black gallstones are not associated with biliary infections and usually form in gallbladder of older individuals. They occur in the following settings:
- increased formation of bilirubin conjugates (e.g. chronic hemolysis in β-thalassemia, sickle cell disease, hereditary spherocytosis)
- ineffective erythropoiesis (e.g. pernicious anemia)
- decreased secretion of bile acids (e.g. cirrhosis)
- ileal pathology (e.g. Crohn's disease, extended ileal resections)
- increased phospholipid synthesis (e.g. carbohydrate-rich diets, total parenteral nutrition)



