Focal Nodular Hyperplasia : Treatment

Comments:
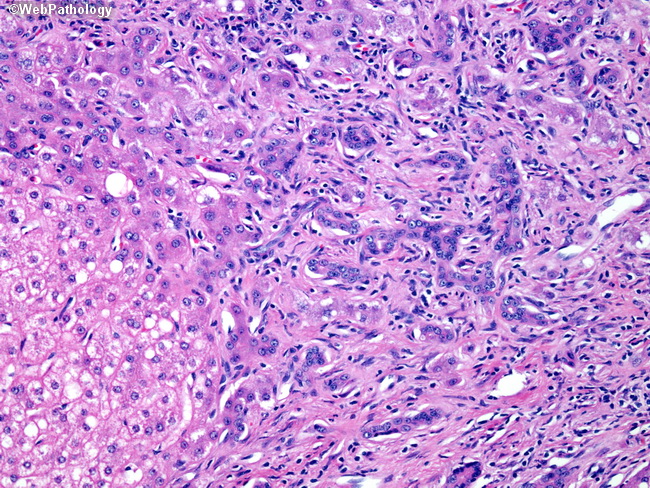
Treatment: Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) remains stable for long periods of time and may even regress. Once diagnosed with imaging, the smaller asymptomatic lesions can be safely left alone. Oral contraceptives (if being taken by the patient) should be discontinued, although there is no convincing evidence of relationship with OCP use.The lesion is monitored with periodic ultrasound. Larger, symptomatic lesions, pedunculated lesions, or those that continue to grow should be removed by segmental resection or enucleation. Another indication for surgery is if the lesion cannot be confidently differentiated from hepatocellular adenoma or carcinoma on biopsy and/or imaging. Recurrences are rare. There is no risk of malignant transformation. About this image: The fibrous stroma of FNH typically contains bile ductular structures (which can be highlighted by CK7 and CK19) and a chronic inflammatory infiltrate. Hepatocytes at the stromal interface may show mild reactive atypia with enlarged nuclei and prominent nucleoli. Foci of marked atypia or increased mitotic activity suggest an alternative diagnosis, such as atypical hepatocellular adenoma or hepatocellular carcinoma.



