Juvenile Polyp with Dysplasia

Comments:
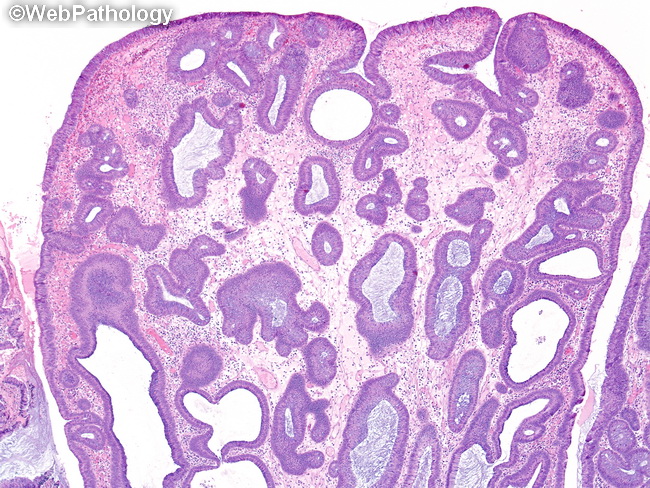
In juvenile polyposis syndrome, there is increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma due to dysplastic epithelium with a juvenile polyp or in a coexistant adenoma. About 30% to 50% of individuals develop adenocarcinoma by age 45. This and the next two images show a juvenile polyp from a patient with juvenile polyposis syndrome. The lining epithelium is dysplastic and resembles that seen in tubular adenomas. Note the distorted and cystically dilated glands and the expanded edematous lamina propria.



