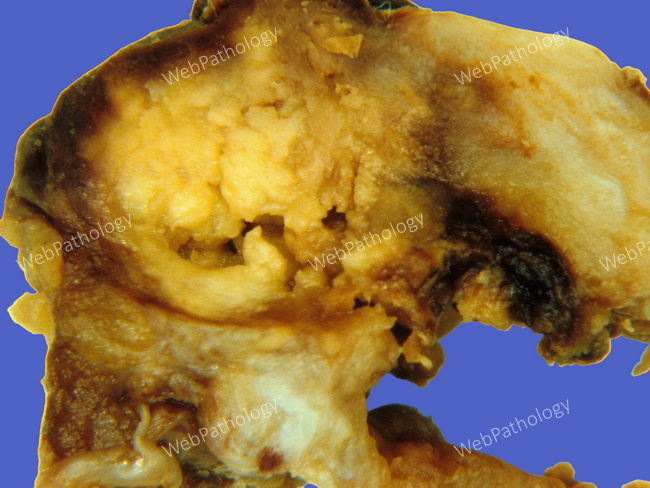
Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis

Comments:
Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis (XC): The inflammatory infiltrate and fibrosis form tumor-like, solid yellow-tan areas that can mimic gallbladder carcinoma macroscopically (as seen in this case). Adding to the confusion, the inflammatory process frequently involves contiguous structures, producing serosal adhesions. CA19-9 may also be elevated. The pathogenesis of XC is multifactorial. Leakage of bile into subepithelial tissues through mucosal ulcers/fissures caused by gallstones or through ruptured Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses plays a role. Bile incites a vigorous histiocytic response. Obstruction to bile outflow by calculi and bacterial infection also contribute to xanthogranulomatous reaction. Bile cultures grow enterobacteria in about 50% of cases. Image courtesy of: Dr. Ibrahim Zardawi; used with permission.



