Ganglioneuroma : Intro & Gross

Comments:
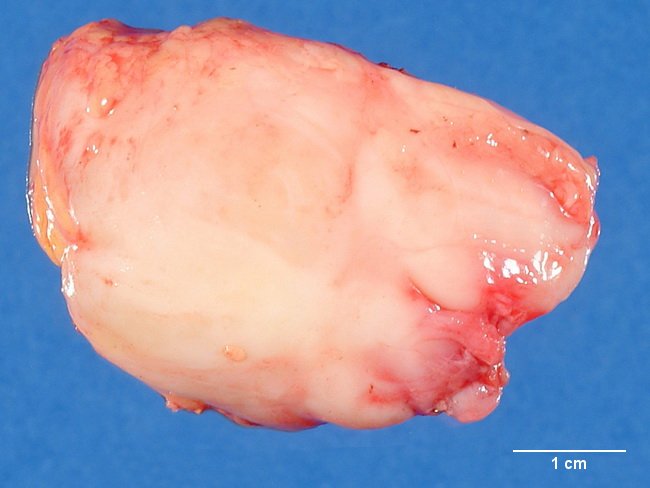
The most common locations for ganglioneuromas are posterior mediastinum and retroperitoneum followed by adrenal gland. Other sites include skin, pharynx, paratesticular region, and gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal Ganglioneuromas: Intestinal ganglioneuromas occur in two settings: 1) Sporadic: as solitary lesions usually involving left colon in adults (median age 48 yrs.) and not associated with genetic syndromes; 2) Genetic Syndromes: as multiple exophytic polyps (ganglioneuromatous polyposis) or as ill-defined transmural lesions (diffuse ganglioneuromatosis). Ganglioneuromatous polyposis is associated with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. Diffuse ganglioneuromatosis is linked with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B and Neurofibromatosis type 1. Polypoid ganglioneuromas involving the gastrointestinal tract have also been reported in Cowden syndrome and tuberous sclerosis. Grossly, ganglioneuromas are well-circumscribed and have a homogenous yellow-white or pink tan cut surface. Some cases may have trabecular or a whorled appearance mimicking a leiomyoma. Larger tumors may have areas of hemorrhage or necrosis.



