Ganglioneuroma : Intro & Gross

Comments:
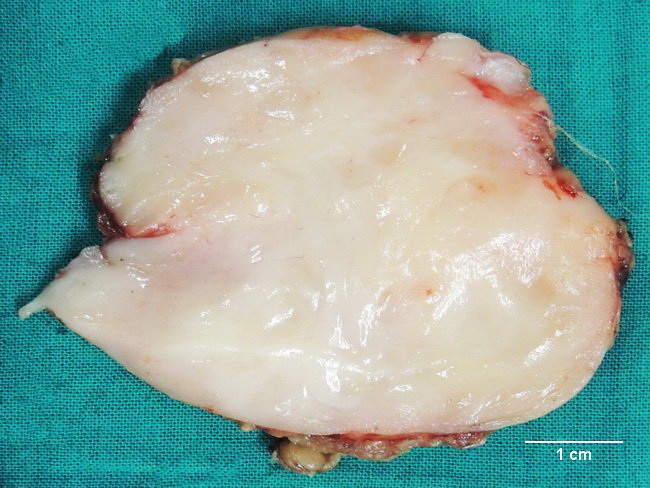
Ganglioneuroma is a benign neuroectodermal tumor that is composed of ganglion cells and Schwann cells. In contrast to neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroblastoma, it contains no immature neuroblastic elements. The most common locations are posterior mediastinum and retroperitoneum followed by adrenal gland. Other sites of involvement include skin, pharynx, paratesticular region, and gastrointestinal tract. Ganglioneuromas tend to occur in young individuals. It is uncommon in those below 10 or over the age of 40 years. In a large series, about 20% of cases involved adrenals. Grossly, ganglioneuroma is well-circumscribed and has a homogenous grayish-white to yellow cut surface with a whorled appearance resembling a leiomyoma. In tumors involving the adrenal gland, thin bright yellow ribbon of adrenal cortex is usually seen stretched over the tumor. This specimen is from a young female who presented with intermittent abdominal pain and diarrhea. Imaging studies showed a retroperitoneal mass at the L1 vertebral level. The excised tumor was well-circumscribed with a fibrous capsule and a fleshy, grayish-white cut surface. Histologic features were typical for a ganglioneuroma. Diarrheal symptoms have been linked to the synthesis of vasoactive intestinal peptide synthesized by the tumor cells. Case courtesy of: Dr. Sanjay D. Deshmukh, Professor of Pathology, Smt. Kashibai Navale Medical College, Pune, India.


