Lipoblastoma : Molecular Pathogenesis

Comments:
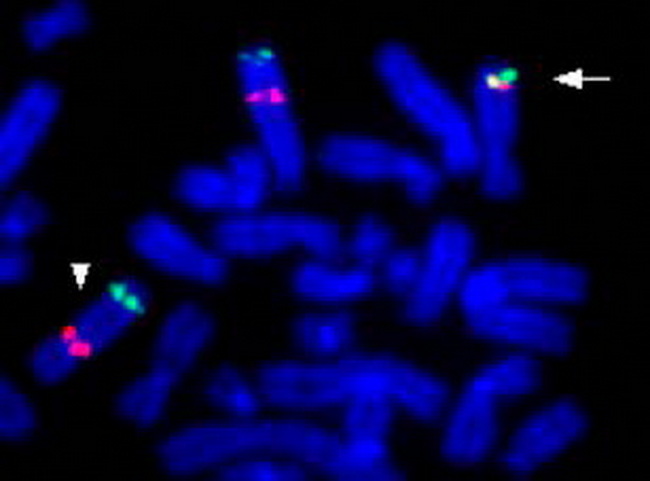
Molecular Pathogenesis: Lipoblastomas consistently show structural rearrangements of 8q11-q13 region (translocation, inversion, insertion, or ring chromosome) that results in the formation of a fusion protein involving PLAG1 and one of many partner genes (>20). Some cases show extra copies of chromosome 8 with or without 8q11-13 rearrangements. In cases with t(2;8)(q31;q12.1) translocation, the fusion partner is COL3A1 on 2q31. Other fusion partners include HAS2 (8q24; shown here), COL1A2 (7q21), RAD51B (14q24), RAB2A (8q12), and BOC (3q13). The constitutively active promoter provided by the partner gene causes upregulation of the PLAG1 which leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation via target genes. The image shows dual-color FISH analysis in a case of lipoblastoma with complex structural rearrangement involving PLAG1 (red signal) on 8q12 and a partner gene HAS2 (green signal) on 8q24. Arrow indicates PLAG1-HAS2 fusion signal on the der(8), arrowhead indicates the normal chromosome 8. Image source: Cristina Morerio & Claudia Panarello, Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology. Image used under: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial No Derivative Works 2.0 France License.



