Calcifying Fibrous Tumor of Gastrointestinal Tract

Comments:
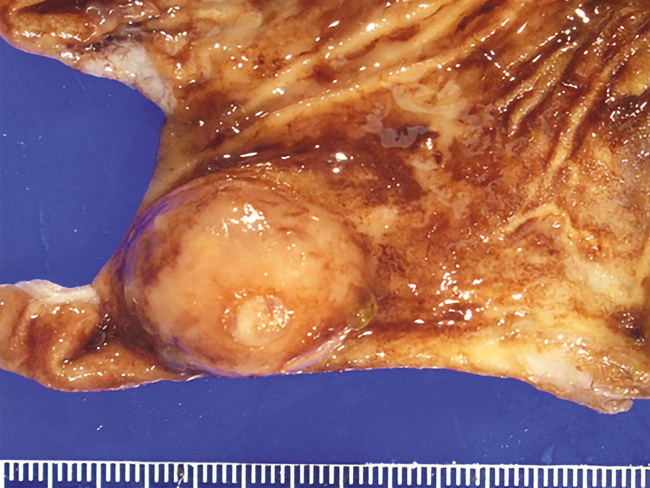
Calcifying Fibrous Tumor (CFT) of the Gastrointestinal Tract: CFT was initially considered to be primarily a mesenchymal tumor of soft tissues. More recently, CFTs have been documented in a variety of sites/organs, including pleura, mediastinum, heart, lungs, neck, spine, oral cavity, paratesticular locations and the gastrointestinal tract. Unlike the CFTs of soft tissues which are usually seen in children and young adults, the CFTs of the gastrointestinal tract have a predilection for adults (median age 49.2 years). They can involve any location from esophagus to colon. They have to be differentiated from other gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumors such as gastrointestinal stromal tumor, leiomyoma, schwannoma, solitary fibrous tumor, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, plexiform fibromyxoma, fibromatosis and sclerosing mesenteritis. The image shows a partial gastrectomy specimen with submucosal calcifying fibrous tumor. Image Source: Turbiville D & Zhang X. Calcifying fibrous tumor of the gastrointestinal tract: A clinicopathologic review and update. World J Gastrol 2020 October 7; 26(37):5597-5605. Image cropped and used under Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.



