Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma : Differential

Comments:
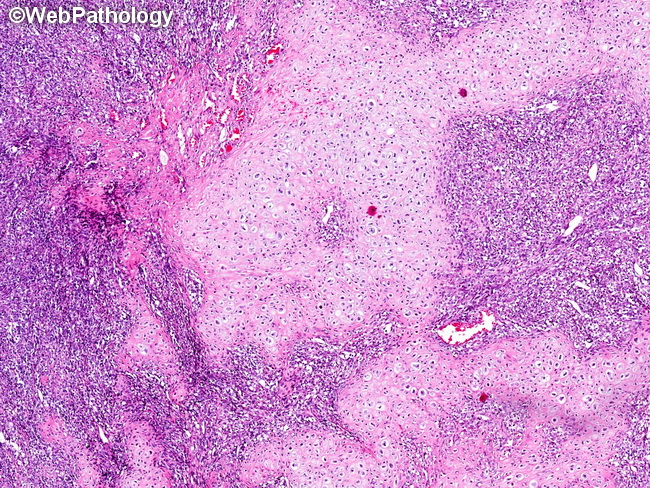
Differential Diagnosis (continued from previous 2 images): Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma (MC) vs Spindle Cell/Sclerosing Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS): MC with expression of myogenic markers (desmin, actin, MyoD1, myogenin) can mimic RMS. Chondroid foci on histology and calcification on radiographs favor MC. In challenging cases, definitive evidence in the form of HEY1-NCOA2 fusion would support MC. Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma (MC) vs Small Cell Osteosarcoma (SCO): SCO may have small foci of chondroid differentiation and staghorn vessels; however they will not show well-developed islands of hyaline cartilage. Delicate lace-like osteoid is present in SCO. Correlation of pathology with imaging findings is a must to arrive at the correct diagnosis. Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma (MC) vs Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma (DDC): DDC shows sharp transition between well-differentiated cartilaginous component and high-grade anaplastic areas. MC often shows gradual blending of the two areas and lacks pleomorphism in the mesenchymal component. DDC occurs more often in the elderly and involves appendicular skeleton. The image shows islands of well-differentiated hyaline cartilage juxtaposed to sheets of small, undifferentiated blue cells. This appearance is virtually diagnostic of MC.



