Plasmablastic Lymphoma

Comments:
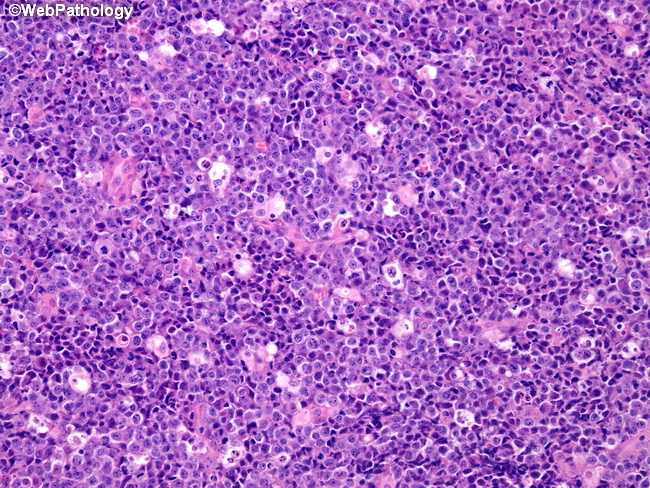
Plasmablastic lymphoma, a highly aggressive variant of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), is seen mainly in immunodeficient patients [HIV (most common), organ transplant recipients, autoimmune diseases]. In HIV+ patients, it presents on average 6 years after the initial diagnosis of HIV. The CD4 counts are usually <200 cu.mm. The most common location is the oral cavity. Other sites of involvement include nasal cavity, gastrointestinal tract, lymph nodes, lungs, skin, bone, and soft tissues. There is a striking male predominance (M:F=7:1) and the median age at presentation is around 39 years. Epstein Barr virus is detected in 75% of cases and human herpesvirus-8 in 16% of cases. Initial response to therapy may be good, but it has poor long-term prognosis. The tumor is composed of sheets of plasmablasts with a starry sky pattern as depicted here.The tumor cells are large with eccentric nuclei, single central prominent nucleolus, and abundant basophilic cytoplasm. Mature plasma cells are rare. Mitotic activity and apoptosis are prominent.


