HPV Transmission

Comments:
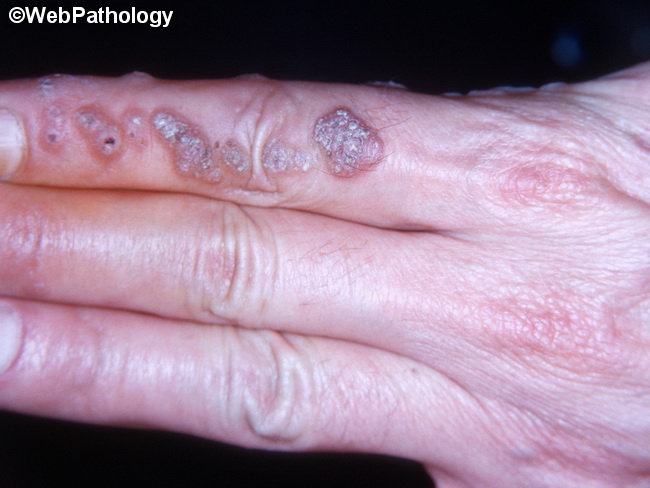
Transmission of HPV occurs via close contact. Viral particles are released from the surface of papillomatous lesions. Minor trauma allows virus entry into skin and mucosal sites and facilitates autoinfection at other sites or within different hosts. Most HPV genital infections are transmitted sexually by minor trauma during intercourse. They represent the most common sexually transmitted disease in the US. Men whose sexual partners have HPV-related cervical lesions have an increased incidence of condylomas. Transmission occurs more readily from females to males than from males to females. The incubation period is 2 to 3 months. Once an infection occurs, autoinfection is common. Most penile HPV infections in men are subclinical and do not result in an HPV-associated disease. Humans can also act as asymptomatic carriers of HPV. Women with anogenital warts may transmit the virus to the baby during vaginal delivery. These children are at risk of developing juvenile laryngeal papillomas, usually caused by HPV6 and HPV11 (the most common agents for anogenital warts). This image of common warts (verruca vulgaris) shows numerous elevated firm lesions with rough surface on index finger of an adult male.



