HPV Genome

Comments:
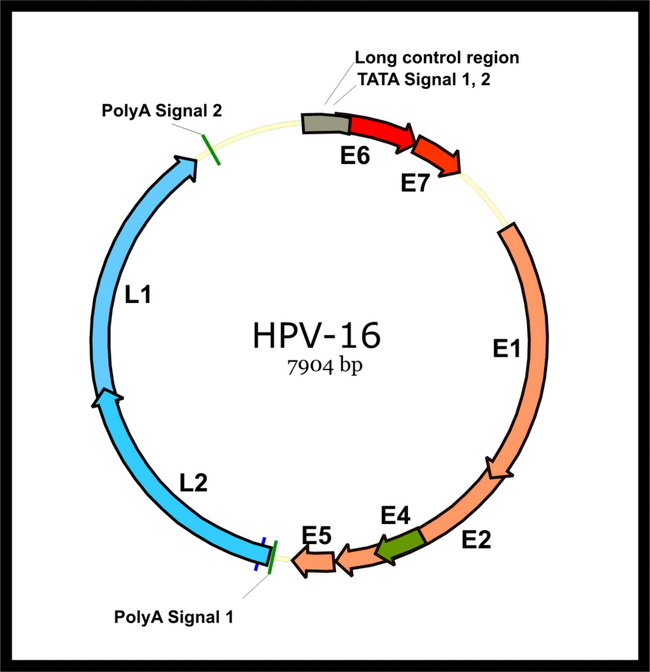
HPV genome is a circular strand of double-stranded DNA of about 8000 base pairs. It has 3 functional regions: a noncoding upstream regulatory region (URR)(aka long control region) of about 1000 base pairs, an early region, and a late region. The URR contains the origin of replication, promoter elements and enhancer sequences. HPV expresses more than 20 mRNAs which synthesize 8 well-characterized proteins in a differentiation-specific and cell-specific manner. E6 and E7 are oncoproteins that interact with and inactivate tumor suppressor genes p53 and Rb. E1 and E2 are viral replication proteins. E4 encodes a protein that disrupts cytoskeletal/keratin framework causing koilocytosis. L1 and L2 are major and minor viral capsid proteins respectively. HPV replication: The papillomavirus lifecycle is initimately associated with epithelial cell differentiation. Viral DNA replication and expression of early genes occur in the stratum spinosum layer of epidermis. Capsid production (expression of late genes) takes place in the granular cell layer. The final steps in viral assembly require fully-differentiated keratinocytes. HPV Genome: Image Source: Xmort / CC BY-SA



