Systemic Mastocytosis : Bone Marrow

Comments:
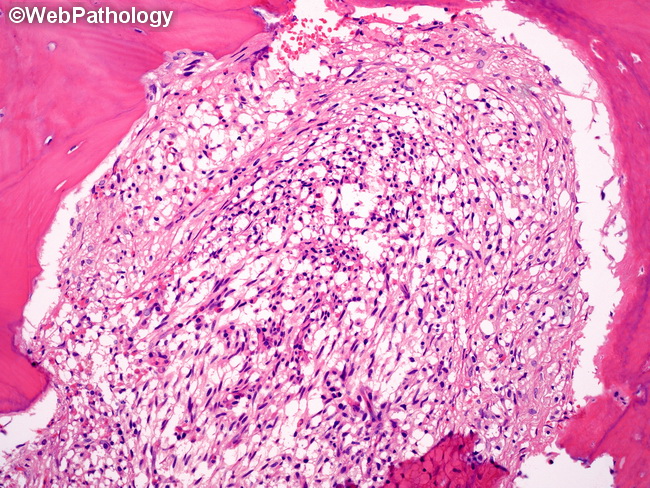
Bone Marrow Involvement in Systemic Mastocytosis (SM): Four major patterns of involvement are seen: 1) Compact mast cell infiltrates (focal or multifocal) - usually seen in indolent systemic mastocytosis and systemic mastocytosis with associated hematologic neoplasm. 2) Diffuse interstitial, consisting of loosely scattered mast cells. Seen in mast cell hyperplasia (MCH) as well as cutaneous mastocytosis. In contrast to MCH, there are greater number of mast cells in mastocytosis. Presence of mast cell aggregates/clusters favor mastocytosis over MCH. 3) Diffuse-compact, with complete effacement of normal bone marrow architecture. Usually seen in mast cell leukemia, and some cases of smoldering systemic mastocytosis and aggressive systemic mastocytosis. 4) Mixed (focal and diffuse interstitial) - usually seen in aggressive systemic mastocytosis and mast cell leukemia, and some cases of smoldering systemic mastocytosis. The patient shows clinical signs of bone marrow failure. The image shows a compact infiltrate of spindled mast cells in the bone marrow from a case of indolent systemic mastocytosis. See previous slide for clinical history.



