Comments:
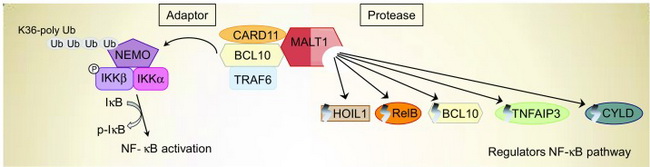
Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Translocation Protein 1 (MALT1) is a caspase-like protease that is encoded by MALT1 gene located on 18q21.32. It has several functional domains, including an N-terminal death domain, three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, and a proteolytically-active caspase-like domain. It plays a key role in BCL10-induced activation of NF-κB signaling pathway and is crucial for the activation and proliferation of B and T lymphocytes as well as production of interleukin-2. Through its adaptor function, MALT1 recruits CARD11/BCL10/TRAF6 complex and activates NF-κB pathway. Through its protease activity, MALT1 regulates NF-κB pathway by promoting degradation of both negative regulators (TNFAIP3, CYLD) and positive regulators (BCL10, HOIL1, RelB) of this pathway. Upregulation of MALT1 expression (as a result of a genetic lesion) leading to constitutive activation of NF-κB pathway is a key event in the pathogenesis of MALT lymphomas. Image source: Schreuder MI et al. Novel developments in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of extranodal marginal zone lymphoma. J Hematop. 2017 Dec. 10(3-4): 91-107. Cropped from the original and used under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.