Rhabdoid Tumor : Role of SMARCB1 (INI1)

Comments:
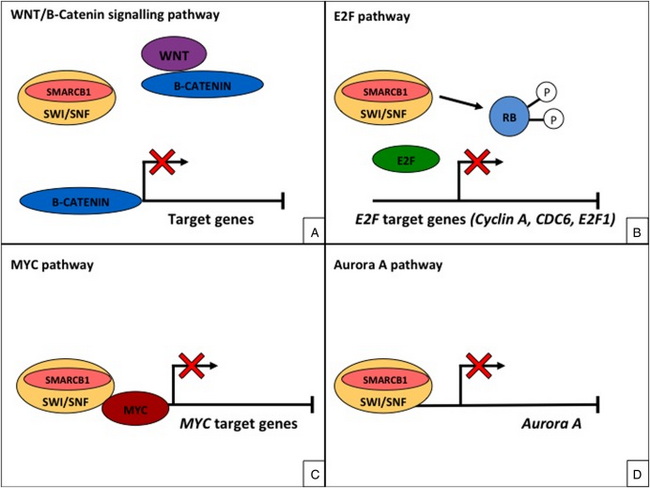
Interaction of SMARCB1 with WNT-β-catenin, c-MYC and Aurora A: WNT-β-catenin signaling pathway: WNT signaling pathway can be categorized into: the canonical WNT (or β-catenin-dependent) and non-canonical WNT (or β-catenin-independent) pathway. The canonical WNT signaling pathway is important in regulating cell fate, proliferation and survival, and its aberrant activation is found in several types of human cancer. The non-canonical WNT signaling is more associated with differentiation, cell polarity and migration. SMARCB1/INI1 is a negative regulator of the canonical WNT pathway and its deficiency results in aberrant activation of this pathway and overexpression of β-catenin. c-MYC: SMARCB1 downregulates c-MYC - a gene that codes for a transcription factor, plays a role in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cell transformation. c-MYC is significantly upregulated in SMARCB1/INI1-deficient malignant rhabdoid tumors. Aurora A: Aurora A, a member of a family of mitotic serine/threonine kinases, is involved in a series of steps during mitosis and meiosis, the proper functioning of which are critical for healthy cell proliferation. SMARCB1 downregulates Aurora A. SMARCB1-deficient tumors therefore overexpress Aurora A.Image source: Kalimuthu SN, Chetty R. Gene of the month: SMARCB1. J Clin Pathol 2016; 69:484-489; used under Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.



