Yolk Sac Tumor : Differential Diagnosis

Comments:
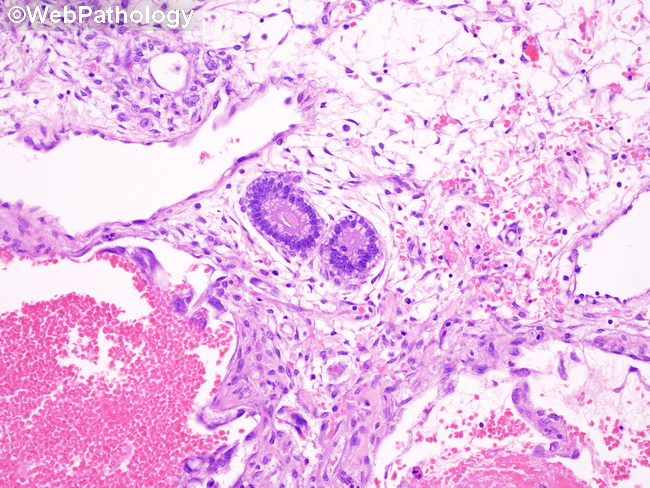
Yolk sac tumor (YST) in adults has to be differentiated from primary ovarian carcinomas.
Clear Cell Carcinoma (CCC): CCC shows tubular, cystic, and papillary growth patterns; presence of endometriosis in the background favors CCC; positivity for CK7, EMA, and PAX8; negative for AFP, glypical-3, and SALL4; reticular/microcystic/polyvesicular areas and Schiller-Duval bodies favors YST
Endometrioid Carcinoma (EC): EC will show other components such as squamous and mucinous areas; background of endometriosis; YST with endometrioid pattern shows greater pleomorphism and mitotic activity than EC.
Dysgerminoma: Solid YST can closely resemble dysgerminoma. Features favoring YST include - greater nuclear pleomorphism, positivity for cytokerain, AFP, and glypican-3. Features favoring dysgerminoma include inflammatory cells in the fibrous septae and positivity for OCT4.



