Cardiac Rhabdomyoma & Tuberous Sclerosis

Comments:
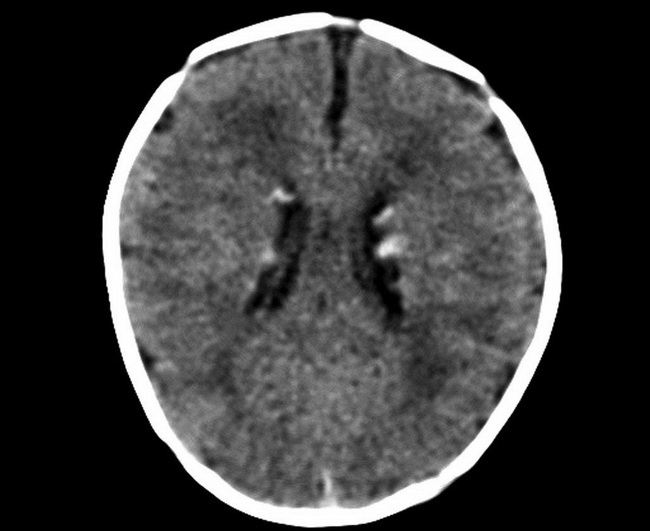
Characteristic neurologic lesions of tuberous sclerosis complex seen on brain MRI include: cortical tubers, subependymal nodules, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, and cerebral white matter radial migration lines. Molecular Genetics:The mutations in tuberous sclerosis complex may be in one of two tumor suppressor genes - TSC1 and TSC2. TSC1 on chromosome 9q34 codes for hamartin. TSC2 on 16p13 codes for tuberin. Hamartin and tuberin form a complex that activates GTPase-activating protein which in turn inhibits mTOR pathway. mTOR is a highly specific protein kinase that regulates protein synthesis, cell differentiation, growth and cell migration. Mutations in either TSC1 or TSC2 result in constitutive activation of mTOR pathway causing abnormal growth and tumor formation. Case History: A child with multiple cardiac rhabdomyomas in the setting of tuberous sclerosis. This axial CT scan of the brain (post-contrast) shows subependymal calcified nodules. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 6290



