Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma : HEY1-NCOA2 Fusion

Comments:
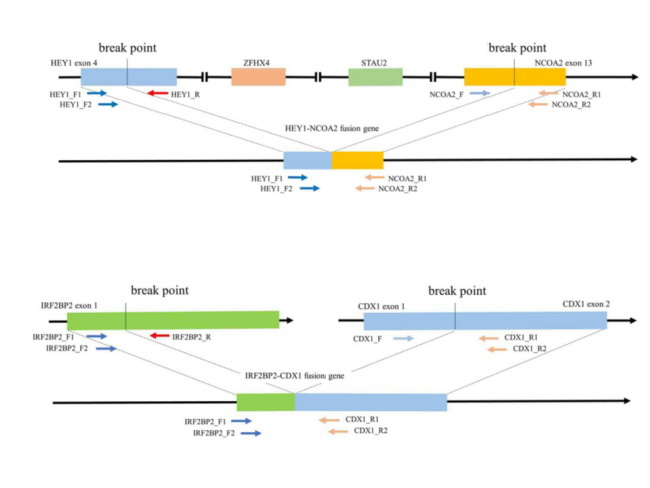
HEY1-NCOA2 Fusion: HEY1 (hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1) is located on chromosome 8q and codes for an evolutionarily conserved protein that is a member of Notch signaling network. It acts as a transcriptional repressor by direct DNA binding as well as by epigenetic modulation. HEY1 affects several downstream genes and pathways involved in musculoskeletal, neurological, and cardiovascular development. NCOA2 (nuclear receptor coactivator 2) is located on chromosome 8q, belongs to the p160 nuclear coactivator family, and encodes a transcriptional coactivator protein for nuclear hormone receptors. It plays a role in transcriptional activation of specific genes as well as in chromatin remodeling. The chimeric fusion results from an intra-chromosomal deletion between exon 4 of HEY1 and exon 13 of NCOA2 (top half). It is present in almost 90% of mesenchymal chondrosarcomas (MC) and can be detected by RT-PCR, FISH or genome-wide screen of exon-level expression.Besides MC, rearrangements involving NCOA2 have been identified in several solid tumors (infantile spindle cell rhabdomyosarcomas, soft tissue angiofibromas, breast and lung adenocarcinomas, melanoma, and urothelial carcinoma of bladder) as well as hematologic malignancies such as acute myeloid leukemia. NCOA2 upregulation is also seen in primary and metastatic prostate cancer. Rare cases of MC show t(1;5) resulting in IRF2BP2-CDX1 fusion (bottom half). Image source: Yamagishi A et al. Primary Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma of the Kidney without HEY1-NCOA2 and IRF2BP2-CDX1 Fusion : A Case Report and Review. Oncology Letters January 2020, Volume 19, Issue 1, p. 885-891; image cropped and used under Creative Common Attribution License.



