Leydig Cell Tumor : Molecular Genetics

Comments:
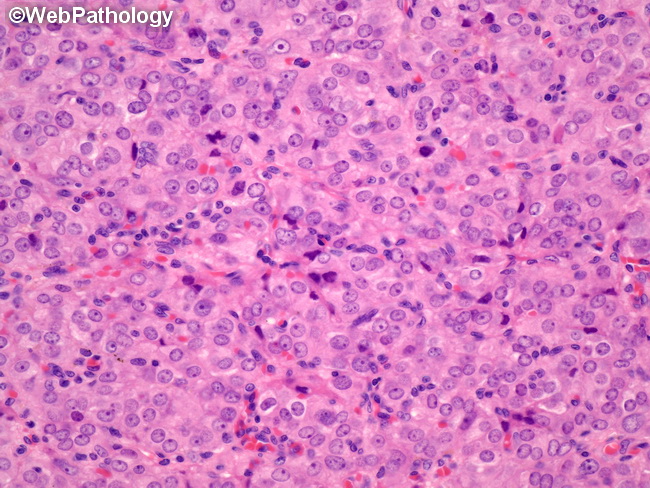
Molecular Genetics: The etiology of Leydig cell tumor (LCT) is unknown in most patients. Rare cases have mutations in the fumarate hydratase (FH) gene either sporadically or as part of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome. Some childhood Leydig cell tumors have acquired activating missense mutations in the luteinizing hormone receptor gene. The image shows LCT composed of diffuse sheets of uniform round or polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm resembling mature Leydig cells. The nuclei are round, uniform, and variably-sized and have prominent central nucleoli. Cytologic atypia is absent and the mitotic activity is not increased. The tumor cells are surrounded by delicate vasculature.



